Quantum-Safe HTTPS Certificates: Google’s Structural Innovation, Technical Foundations, and Governance Implications
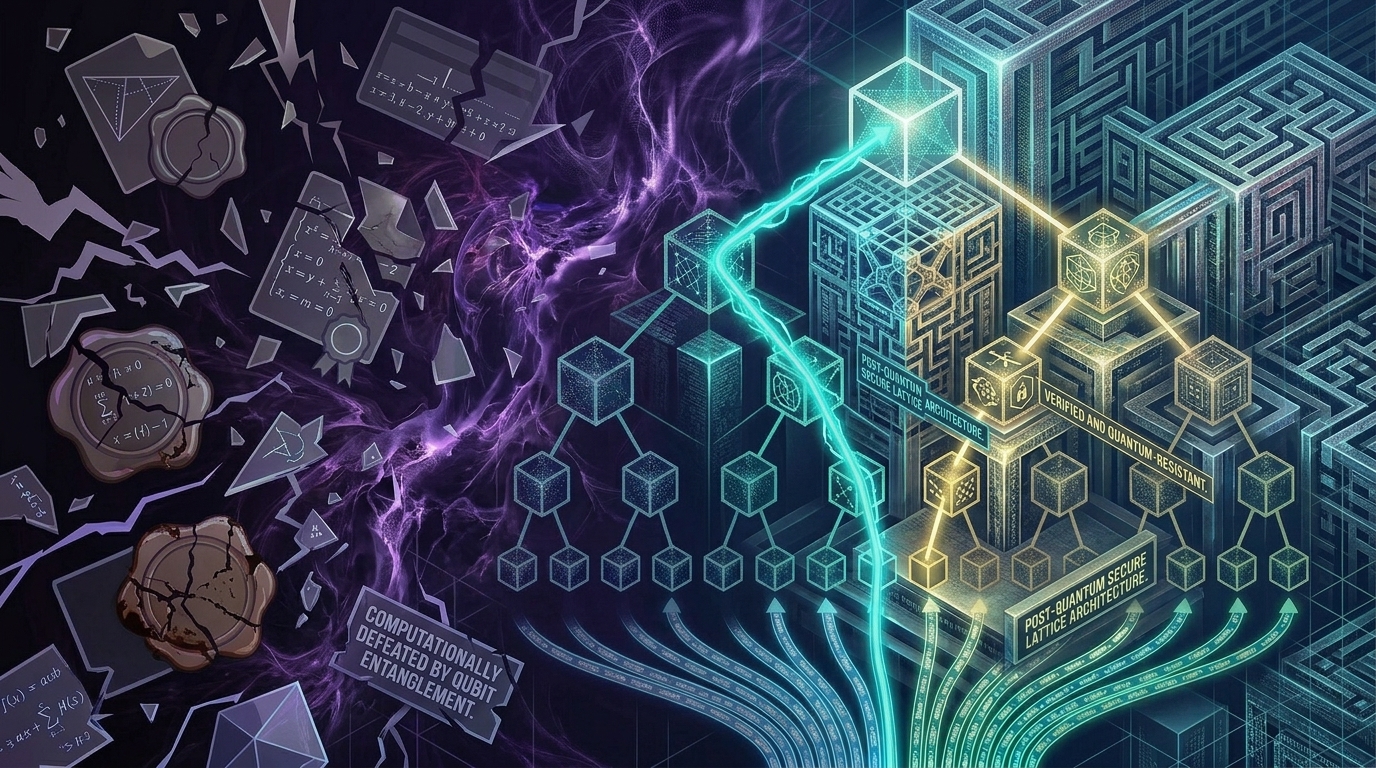
The security of the modern web depends on public key cryptography embedded in the TLS protocol and the Web Public Key Infrastructure. These systems rely primarily on RSA and elliptic curve signatures whose security rests on mathematical problems believed to be hard for classical computers. The emergence of quantum computing challenges these assumptions. Shor’s algorithm shows that sufficiently powerful quantum computers could efficiently solve integer factorization and discrete logarithms…
| Keywords | post-quantum cryptography, WebPKI, TLS, Merkle trees, certificate transparency, authenticated data structures, Internet security architecture, quantum resistant cryptography, cryptographic scalability, transparency logs |